Semiannually – What Is Semiannual?
 Semiannually describes something that is calculated, paid, reported, published, or otherwise occurs twice each year or once every six months.
Semiannually describes something that is calculated, paid, reported, published, or otherwise occurs twice each year or once every six months.
Biannual or semiannual simply means that something occurs twice a year. For example, a company could have company celebrations semiannually. The first is the company picnic over the 4th of July Holiday weekend. The second is the company Christmas party held the last Saturday each year. If a family takes a summer holiday vacation and a winter holiday vacation, they do so semiannually. Anything that happens twice a year occurs semiannually.
Corporations can pay semiannual dividends to their shareholders. In that case, the shareholders receive dividends twice each year. Corporations are free to choose how many dividends to distribute each year or none at all. Financial statements or reports are frequently published on a quarterly basis. Quarterly means four times per year, or once each quarter. It is rare that corporations publish financial statements only semiannually. They do, however, publish an annual report, which, by definition, occurs once every year.
Why Semiannually Matters
Semiannual payments are important to understand regarding investments. For example, when purchasing bonds, they are usually described by the yield they pay the bondholder.
A $2,000 bond could have a yield of 5%. It is important to know if this 5% is paid annually or semiannually to understand the payment you would receive as the bondholder. For example, if the bond paid the yield annually, the bondholder would receive $100 a year. Now, if the bond paid the yield semiannually, the bondholder would receive $200 a year. This is an important distinction to note when purchasing bonds. For example, U.S. Treasury bonds pay a yield semiannually. (Source: investopedia.com)
Interest Compounded Semiannually
Compounding interest semiannually means that the principal of a loan or investment at the beginning of the compounding period, in this case, every six months, includes the total interest from each previous period. This is different from simple interest calculations. In simple interest loans and investments, the amount of interest owed is based only on the initial principal amount. When interest is compounded, the interest from every previous period is added to the principal. In compound interest loans, you are paying interest on interest. Conversely, if you have an investment that compounds interest, you are paid interest on the interest.
When interest is compounded semiannually, it means that the compounding period is six months. Compounding periods can range from daily to annually. The more often the interest is added to the principal, the higher the total interest over the life of the loan or investment. For example:
If you have a five-year loan that compounds interest semiannually, the total interest up to that period is added to the principal nine times. The first compound period does not have any interest added to the principal because no interest was accrued. For the second period, the interest from the first period is added to the principal. In the third period, the interest from the first two periods is added to the principal. This pattern continues over the life of the loan. (indeed.com)
Semiannually vs Biannually
Biannual and semiannual are synonyms, which means that they have the same definition. Although some synonyms are similar with slight differences in implied meaning or usage, these two words are nearly interchangeable.
Technically there is a slight difference in meaning. Biannual means twice a year. Semiannual means every six months since the prefix semi means every half year. This, however, is such a small distinction that it is widely accepted to use these terms interchangeably.
Also, you may see this word with a hyphen, semi-annual, or written as two words with a space between each, semi annual. Both of these are common errors and should be avoided.
Semiannual vs. Biennial
Semiannual is an adjective that describes something that happens twice in a single year. However, biennial is a word that describes something that happens every other year. Often, biennial is confused with the word biannual, which means the same thing as semiannual. Biennial means something that happens every other year. Biannual and semiannual mean the same thing – something that happens twice per year.
Example of Paid or Reported Semiannually
For example, a ten-year municipal bond is issued by Los Angeles, California, in 2015. It pays interest semiannually each year until the bond’s maturity date in 2025. Investors who buy these bonds receive interest payments twice in each of those years. Payments are made once in January and once in July. The city also publishes a semiannual report on its finances, once in March and once in September.
Up Next: What Is a Lorenz Curve?
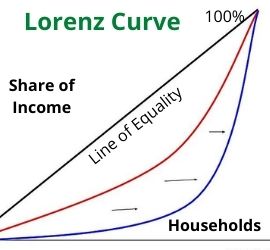 The Lorenz curve is a graphical representation showing the distribution of income or wealth within an economy developed by Max Lorenz in 1905.
The Lorenz curve is a graphical representation showing the distribution of income or wealth within an economy developed by Max Lorenz in 1905.
The Lorenz curve is a way to measure income distribution. The curve graphs cumulative percentages of income on the Y-axis. It presents distribution as cumulative percentages of households on the X-axis. If each group earns their share of the national income the Lorenz curve will be a straight line at a 45° angle. This is called the line of equality. For example, the bottom 10% earn 10% of national income, the bottom 50% earn 50%, and so on.
An economy with an unequal distribution of income will create a Lorenz curve that is bowed out from the line of equality. For example, the bottom 25% earn 3% of national income, the bottom 50% earn 12%, and so on. Economies with a Lorenz curve farther from the line of equality have a less equal distribution of income. Conversely, economies with a Lorenz curve closer to the line of equality have a more equal distribution of income.




